Nits and lice look so specific that, having seen them once, it is impossible to forget the sight. Louse is an external type of parasite that feeds on human blood and is a peddler of typhus and relapsing fever, as well as Volyn fever. Nit is the larva or the bloodsucker's egg.
When infected with insects, pediculosis is diagnosed. The disease takes its name from the Latin word pediculosis (lice) and has characteristic symptoms. Children of 3–6 years of age and adults from socially non-adapted families are often ill. But lately, parasites are often found in prosperous citizens. Despite the prevalence of pediculosis, many people still came across it and do not know what lice and nits look like in the head, how to get rid of them and why they appear.
Types and forms of nits
Pediculosis causes three types of parasites, headaches, pubic and ward. They differ in shape, size and localization features. Their eggs are called nits regardless of the variety. Distinguish types of bloodsuckers can be by the presence of characteristic signs.
Cause the most common form of lice. Insects parasitize and breed in the area of the hairy part and do not leave its limits. The head louse eggs are located mainly in the region of the crown, occiput and temples. This is caused by a comfortable temperature for their development due to the proximity of the vessels in these parts of the head. Unlike other species, head bloodsuckers prefer high temperatures and do not leave the host even during fever.
See how the nits look on the hair, you can without a microscope. The adult female has sizes from 2 to 3.5 mm, the male can grow up to 3 mm. Having reached sexual maturity, the louse clings to the hair with its paws and lays the larvae, firmly fixing them with sticky substance. It feeds on blood, periodically sucking it out of the skin. Fasting can not longer than a day. At uncomfortable temperatures below plus 20 degrees, the female stops laying.

Egg size is not more than 0.8 mm. During the day, the female reproduces up to 4 nits. Embryo development is 9 days. The total period of conversion of an egg into an adult louse is about 16 days. The female itself dies in one month, having time to postpone up to 140 larvae.
Among the main characteristic signs of head nits can be noted:
- capsule round shape,
- light or grayish color
- good fixation to the hair,
- squeezing when crushed
- localization in the temples and neck of the head.
With severe lice, there are a lot of eggs and they look like small white or grayish dots. Especially noticeable bright eggs on black hair. With inexperience, the larvae are confused with dandruff. On an enlarged photo of this type of nits, a capsule with a slightly convex lid and an embryo under it is clearly visible.
On a note! Head nits and adults parasitize only on the person and do not live on linen and animals.
This type of lice is less common. Previously, soldiers suffered from wounded pediculosis, now prisoners and socially disadvantaged people. To see how the eggs of the type of lice look like, you can examine the seams of clothing infected. It is there that parasites hide.

They are quite large and can fast up to 3 days at a temperature below + 30 degrees, and at + 10 they do not eat a week. Females in length reach 0.5 cm, males 3.5 mm. They leave the seams only for the purpose of feeding and reproduction. Ware larvae are attached to the pile of underwear and in rare cases on small hairs of the body.
The egg on average reaches 1 mm in diameter. With its increase visible flattened cap and embryo under it. The life cycle of lice lasts from one month to 60 days depending on the conditions.
On a note! The causative agents of ward lice leave the host with a fever above 38.5, if they are typhoid fevers, it contributes to the development of the epidemic.
Infection with representatives of this type is unreasonably considered shameful due to sexual transmission. But pubic lice has a slightly inappropriate name, given its real localization. Lice eggs on the hair are found in this disease not only in the pubic hair, but also in the armpits, eyebrows, eyelashes. If you have a mustache, beard and chest hair, you can see the larvae there. And the risk of infection exists without sexual intercourse.

The causative agent of pubic lice is a louse-ploschitsa. It has a small size, short oval body. In the enlarged picture of the ploshchitsa, legs with curved claws are clearly visible. They help the parasite to stay on the hair. What a pubic louse nit looks like is difficult to see without magnification. Its size is only 0.5 mm and it looks like a grain of sugar, but in form resembles a pear. When localized on the eyebrows and eyelashes, it seems that the hairs are sprinkled with semolina. Eggs develop favorably at temperatures from +20 to +40.
In children, this type of pediculosis is diagnosed in rare cases. Localization is more common in the region of the eyelashes and eyebrows, which causes inflammation of the eyelids and eyes (blepharitis and conjunctivitis).
Many are interested in what color lice and whether they differ depending on the type. Adults of the head parasite have a different color, more often they are light gray, but they are also dark. Body lice are always yellowish, pubic almost white. Insects can change color depending on the degree of blood saturation of the host.
Causes of nits and lice
The main cause of any pediculosis in medicine is officially recognized as a violation of sanitation and personal hygiene. Maximum infestation with head lice is recorded in the summer. This is due to favorable temperature for their reproduction, swimming in water and traveling by train.

In children, it is possible to detect nits in the hair regardless of the season. The factor of infection in them is associated with being in a team. Most often sick children from 3 years and children up to the age of 14 years. Head lice quickly from a sick person to a healthy one. It is possible:
- by close contact with infected people,
- through clothes, especially hats,
- when using alien combs, scourers, elastics and pins to hold the hair.
- while visiting the pool and sauna,
- when traveling by train and overnight at train stations.
In water, lice do not die up to 2 days. Therefore, with frequent swimming it is necessary to constantly inspect the head for the presence of parasites. It should be borne in mind that nits enter the head only from an adult female.
Attention! If lice eggs are found on the hair of the head, then there must be an adult that laid them off.
The pubic species is infected predominantly through sexual contact when in contact with the patient. But it is possible to pick up such insects even when using hygiene items and underwear alone. Most often they suffer from persons without a certain place of residence and asocial personalities (drug addicts, alcoholics).
Worn lice can become infected by using someone else’s underwear or bed linen.
Symptoms and signs
The clinical picture of pediculosis is similar in different types of pathology. The main symptom is severe itching caused by the saliva of the parasite. The presence of adults and nits lice confirms the diagnosis of 100%. For any pediculosis:
- sores and purulent wounds appear at the site of scratching,
- developing dermatitis and eczema,
- in the case of a secondary infection, the temperature rises, and the regional lymph nodes become inflamed,
- disturbed sleep and psychological balance in the body,
- nervousness increases.

When the head is localized, the hair becomes dull, they contain "mats". When running pediculosis, the temples and the back of the head acquire a whitish hue due to the abundant seeding with nits.
The same changes in the region of the eyelashes and eyebrows are characteristic of the pubic type. Small hairs are filled with eggs, stick together and gradually break without treatment. The appearance of the patient becomes repulsive and unpleasant.
When mixed form of pediculosis, clinical signs appear in a complex. Lice are found in the head, body, and clothing. Identify the pathogen can only be examined by examining the egg lice under a microscope.
Methods for getting rid of nits and lice
It is recommended to treat head lice with special insecticidal agents. When they are intolerable, they use a mechanical method of getting rid of eggs and adult parasites. In children and pregnant women, therapy should be especially safe. Until the age of 5 years is better not to use chemistry. Boys can be trimmed naked, and girls can have a short hairstyle and destroy the lice and nits manually.

- Mechanical method. It consists in combing insects with a fine comb. To do this, put light paper on the table, bend over it and hold the comb from the back of the head to the forehead. Movement is repeated many times. Eggs cannot be removed in this way. They need to pull out by hand. The larva should be clamped with pads and nails of the first and second fingers and pulled from the hair with a movement from the root to the tip. All adult lice and larvae along with the paper must be burned.
- Chemical method It is used in people with large hair, which does not allow to destroy nits and lice on the head manually. For treatment, special soaps, shampoos, solutions, aerosols and emulsions are used. When the head and pubic localization of pharmaceutical preparations applied to all parts of the body with hair, carefully rubbing the roots. The exposure time depends on the form of the agent. After the procedure, the medicine is washed off with warm tap water. Rinsing is recommended to be carried out with acetic solution (not stronger than 5%). While maintaining the dead nits on the hair, combing is performed with a comb with small gaps between the teeth.
- Physical impact. It is used in the form of lice pediculosis. To destroy lice and eggs, linen and bed boil for at least 10 minutes. The seams of clothes can be ironed with a hot iron. Those who served in the army and suffered from body lice, say that while there are characteristic clicks.
Description and types of insects
Lice are a small gray-brown insect with a length of 1 to 6 mm. They have a flat body with a small head and chest, the main part of which is the abdomen. The wings are almost invisible, but there are 6 legs, with which lice move very quickly.
Depending on the habitat, there are 3 types of lice:
Head louse lives on the scalp, mainly in the occipital region and temples. It has a torso of a grayish tint measuring 2-3 mm. Short tenacious legs allow the insect to move freely through the hair.

Pubic louse is parasitic on the genitals and in the anus, in rare cases it can appear in the armpits. The color of her body is light brown, thanks to which the insect is inconspicuous on human skin.
Body lice are located in the cuffs, seams and folds of clothing that is most closely in contact with the human body. When the feeling of hunger begins, the insect creeps onto the skin and then comes back. Outwardly, they are similar with head lice, have a slightly elongated body of a dirty white color.
Nits are a shell of oval shape of a light yellow color, consisting of 2 parts. The inner part is yolk, the outer is leathery, resembles a cocoon. Female lice lay nits, attaching them to the hair with a special adhesive substance that is resistant to external influences. In the presence of wardrobe head lice eggs stick on the fabric.
The development of parasites on the hair
Female lice that have reached the stage of an adult individual are immediately ready to breed. 2 days after fertilization, she lays 4-5 eggs on her hair. The process of their maturation takes from 5 to 15 days, depending on the ambient temperature. The most favorable temperature is considered to be about + 30 ° C. One female in her life is able to lay from 80 to 150 eggs. Thus, the number of parasites in a couple of months may increase by several dozen times.
 Breeding takes place by laying eggs, which are called nits.
Breeding takes place by laying eggs, which are called nits.
With the help of a microscope, you can see that the nits resemble translucent drops located at a distance of 1-3 cm from the hair root. In the lower part of the nits is a mount that holds it on the hair, and on top - like a lid. The mature larva begins to swallow air intensively. In this case, the gases exiting the anus, push it out. After the release of the young individual empty nit remains in its place.
What color dry and lively nits
On closer examination, living nits can be distinguished from dry nits depending on the color they have. Live white nits with a light yellowish tinge. When hit by a ray of light, they shine a little. For dry nits characteristic dirty yellow dull color.
When you try to crush live nits, a characteristic click is heard, which publishes a burst protective sheath. Dry nits remain tightly fixed on the hair, but when they are crushed there is no click.

Nits on the hair look like white dots that are easily confused with dandruff. For this reason, many people with pediculosis delay treatment. If you have any doubts, it is best to contact a specialist to recognize the type of disease and select medications. Independently distinguish nits from dandruff can be on a number of characteristic signs:
- Nits have a certain oblong round shape, about the same size. Dandruff is a formless flakes of dead skin that are of different sizes.
- Nits are located closer to the hair roots. Dandruff can be dispersed throughout the length of the hair and visible on the clothes of black shades.
- Nits are well fixed on the hair. To remove them, you need to make an effort. Dandruff can be easily brushed off.
- Itching with pediculosis is very pronounced and brings painful sensations. In the presence of dandruff, only slight irritation of the scalp is felt.
Dandruff causes inconvenience only to the person himself and does not pose a threat to others. Pediculosis is a parasitic disease, so it is important to determine in time the presence of lice and nits in order to take measures to destroy them.
Effective methods of struggle
Each nit is covered on top of a protective sheath that is resistant to moisture and special preparations. For this reason, it is much more difficult to fight nits than live adults.
In the presence of pediculosis in men and young children, the easiest way to get rid of parasites is to completely shave off the hair on the head. For aesthetic reasons, this procedure is not suitable for everyone, so there are quite a number of other methods of dealing with nits and lice.
 A female louse that has reached the adult stage is immediately ready to breed.
A female louse that has reached the adult stage is immediately ready to breed.
Folk remedies
Are considered more safe for humans than chemicals. The most popular are:
- Lemon or cranberry juice. It contains a large amount of acid, which is able to destroy the shell of the nits. Lice with such exposure become less mobile. If you wet the hair with juice for several days, then you can easily comb the lice and nits with a comb.
- Onions or garlic. These vegetables have a caustic substance that is detrimental to the parasites. It is necessary to squeeze the juice of onion or garlic, put on hair, keep under a plastic bag for 3-4 hours. Then rinse thoroughly and brush hair.
- Sunflower and lavender oil. In sunflower oil, add a few drops of lavender oil and apply this mixture to your hair. Cover the head with a plastic bag and hold for an hour.The oil film prevents the insects from breathing, which leads to their death.
Treatment with folk remedies takes a long time and does not always give positive results.
Medications
Such tools for the destruction of lice and nits are special shampoos and solutions for treating hair.
The most effective among them are:
- Pedilin shampoos, Paranit,
- aerosols "Nuda", "Couple Plus",
- Medifox emulsion,
- cream "Nittifor".
Often complete with drugs attached special combs used for combing lice and nits. They have metal teeth with special notches. The lumen between the teeth is negligible, which allows you to hold nits and lice.

Combing Removal
Crest Use Rules very simple. After treatment with special hairs, it is necessary to divide them into thin strands. Combing is done from root to tip along the entire length of the hair. To insects could be seen, it is better to perform this procedure over a white cloth.
Using the comb is absolutely safe and has no contraindications. It can also be used for prophylaxis by combing hair once a week to detect parasites.
To completely get rid of lice and nits is most often used a complex method of treatment, including chemicals and mechanical means. Like any other disease, pediculosis is easier to prevent than to cure. For this it is enough to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene.
Nits in humans: what they look like
Blood-sucking insects that parasitize humans, or lice multiply, laying eggs on the host's hair. A parasite develops inside each egg. And in order to preserve their offspring, lice secrete a special secret that reliably attaches the egg to the hair. In addition, each nit is packed in a special shell. Stagnating in the air, it becomes quite durable and reliably protects the developing individual from external influences.
From a biological point of view, calling the offspring of parasites an egg is wrong. In fact, this is only the initial stage of insect development. And she received such a name due to the fact that it has a shell that does not provide the larva with food, but only is a kind of protection for it.

Nits female firmly glues to the hair with glands, and after a few minutes, that it can not be removed even with nails.
Light color makes them more noticeable than adults. And with a strong infection to see how the nits look on the hair can be with the naked eye. They look very similar to dandruff, but, unlike the latter, they are not shaken off. You can remove them using a frequent comb and only after washing with a special shampoo.

Nits are not located along the entire length of the hair. The female sticks an egg at a distance of 2-3 cm from the root.
If we consider the larva under a microscope, then it is a small capsule and, depending on the type of lice, the nits can be elongated or short and round. In the lower part there is a peculiar belt formed from the same substance as the shell itself. The upper part ends with a cap through which the larva hatches. The size of the capsule does not exceed 0.7 mm in length, and the diameter is only 0.4 mm. Therefore, it is impossible to consider whether it is empty or full to the naked eye. Moreover, dry capsules are also firmly held on the hair, like those in which the larva is still located.
And you can get rid of them using the following drugs:
- Vinegar
- Cranberry juice
- Some synthetic acids.
How do the larvae develop?
Females of parasites reach sexual maturity and mate with males after the last molt. And from this point on, each of them lays up to 10 eggs per day. It happens as follows:
- The female, riding her hair, crawls up on it.
- At the same time inside the body begins the process of lowering the larvae through the oviduct to the anus.
- Moving past the glands, it is enveloped in a sticky secret, which is in contact with the human hair securely attaches an egg to it.
- In this part of the fluid flows into the upper part of the capsule, forming a cap.
- After a few minutes of being in the air, the secret hardens and firmly glues the egg to the hair.

In the photo nit under the microscope
The development of the larvae lasts about 8 days at a temperature of 33 ° C. If it drops to 22 ° C or rises to 40 ° C, the process stops. But even at 0 ° C, viability lasts up to 2-3 months. Destructive to nits and lice is a temperature of 45 ° C and above.

On the photo— nit at the moment of louse hatching.
The release of the larvae from the capsule begins with the ejection of the cap. This opens access of oxygen inside. At the same time, it enters not only into the lungs, but is also swallowed, passes through the digestive tract and is released through the anus. This feature leads to an increase in pressure in the capsule and the expulsion of the individual from the egg. Usually it takes several minutes from the time the lid is opened until the insect is ejected. The empty shell remains on the hair and holds on to it as firmly as a full one. And by the way the nits look like in a person, it is impossible to determine if there is an insect in them.
How to look for pests?
Is it so easy to see parasites? It all depends on the type and color of hair. In light and curly hair it is difficult to find practically colorless shells, and in dark and straight they are clearly visible in the form of white grains. They are easy to notice to someone who knows what the nits look like. Most often they are located at a height of 2-3 cm from the root, and one at each hair.

The photo shows how the nits look on the hair with a large number of lice
What is different from dandruff and how do lice eggs look?
Externally, fine white dandruff is very similar to cocoons. And from a long distance to determine that this is impossible. If you look closely, the differences are visible, although not immediately, but only with careful consideration. They consist in the following details:
- Dandruff does not stick to the hair and is showered with a slight shaking.
- The color of the capsules is yellowish with glitter, dandruff is pure white, matte.
Symptoms of Pediculosis Infection
Symptoms of this disease are very characteristic. They appear immediately after infection. At the initial stage - this is: severe itching in the hair of the head. Further secondary signs appear:
- Combs and sores on the scalp
- The presence of white patches of hair roots (nits)
- Some patients have edema of the ear and nasal lymph nodes
- Abundant purulent discharge with severe infection.
In addition, the patient becomes irritable, feels psychological discomfort.

Affected areas of the skin can fester, forming pustules, boils.
Is the disease transmitted from person to person?
Yes, but only with very close contact. In all other cases, insects get from one host to another through hair care items: combs, massage brushes, hairpins, elastics, hairpins.
In other ways, the transfer is excluded. This results from the fact that the larvae hanging on hair are motionless and therefore cannot get from one person to another. But an adult individual is capable of crawling.
Is it difficult to get rid of parasite eggs?
Unlike adults, they are more resistant to the effects of special means. Of the variety of drugs, only having in the composition of organophosphate insecticides to destroy the larvae.
Vinegar also contributes to the softening and destruction of the skin. But it should be used carefully, since at high concentrations it can cause scald scalds.
By adding it to the water to rinse the hair and then combing it with a frequent comb you can get rid of a small part of the eggs, but complete removal will not occur.
Watch the video: What is pediculosis, treatment methods
Pediculosis treatment methods
How to get rid of parasites? Today there are many means and ways to deal with them. And to tell about each of them in one article is impossible. Therefore, we only list the main ones:
- Chemical
- Mechanical
- Combined.
The first involves the use of various protivopedikuleznyh substances. The second one is combing with a frequent comb or manually. The third is the sequential application of chemical first, then mechanical, and is the most effective.

After each treatment of the head, nits need to be combed with a special comb.
Each of them has its advantages and disadvantages. Thus, the use of modern drugs allows you to quickly eliminate the cause of the disease, but with repeated use or exceeding the recommended dose can lead to allergic reactions.
Combing is time consuming. From the first time to remove all the parasites will not work even when using a special metal comb.
In addition, when choosing a specific method, it is necessary to consider the degree of infection. A small number of insects can be removed manually, but if the disease is in an advanced stage, then an integrated approach will be required using the most effective insecticides.
In some cases it is easier to shave off the affected hair than to apply one of the methods described above. This is usually done when pediculosis is found in young children and children. Girls on such a procedure is unlikely to agree. For them, the use of insecticide-based sprays would be more acceptable.
What kind of parasite is a louse?
Today scientists know over six hundred varieties of liceHowever, only two main types can live on a person. At the same time, these insects are quite different from those that are not able to parasitize on the surface of human skin.
To choose the right way to deal with these parasites of the human body, you should know exactly what the lice and nits look like in humans.
Tired of pest control?
At the cottage or in the apartment cockroaches, mice or other pests started? They need to fight! They are carriers of serious diseases: salmonellosis, rabies.
Many summer residents are faced with pests that destroy the crop and damage the plants.
In such cases, our readers recommend using the latest invention - Pest Reject repeller.
It has the following properties:
- Eliminates mosquitoes, cockroaches, rodents, ants, bedbugs
- Safe for children and pets
- Runs on line, no charge required.
- No pest control effect
- Large area of the device
Today it is considered that there are three key types of lice that can parasitize on the surface of the human body - pubic, head and dress.
With the exception of the latter, all presented species live in close proximity to human skin, being at the same time carriers of various kinds of diseases. Due to their bites, a certain irritation occurs, which is accompanied by severe itching and other unpleasant sensations.
Head lice
This type of insect is one of the most common in humans living in standard conditions. Such lice in most cases live in the scalp, but they can also be found in whiskers, and in particularly neglected cases even in the beard of men.
Such parasites feel great in the human scalp, which affects their active reproduction. They are not afraid of high temperatures, so louses can feel excellent even at temperatures of about 40 degrees.
The main distinguishing feature of this species is that in the absence of hair, they are not able to exist.
Body lice
Otherwise, these lice are called underwear. In appearance, they are very similar to head lice, differing only in color, which can range from off-white to dull-yellow. Lice of this type live in everyday clothes of a person, but cannot live on the body or in the hair.
As a rule, there are a lot of such lice in the homeless or in people who do not have the opportunity to regularly change clothes. They drink human blood, clinging, as a rule, to those parts of the body where the hairline is not too large. Dealing with louse clothes is much easier.
Pubic lice
In most cases, live in the human groin, but in certain cases, pubic lice can live on the eyebrows and eyelashes.
 Stories of our readers!
Stories of our readers!
“We spend the whole summer at the dacha, there are a lot of mosquitoes, flies and midges. It’s impossible to be in the house, and even more so on the street, neither to adults nor to children. We bought a trap lamp according to the advice of neighbors.
We use the lamp for more than a month. Lost of flying insects and often in the evenings outdoors. Very pleased with the result. I recommend to everyone."
What do lice and nits look like?
The size of the lice that live on humans can be about 4 mm, and the larvae are approximately half the size. The surface of the larvae is covered with sticky mucus, thanks to which they are firmly attached to the hair at a distance of about two to three centimeters from the surface of the skin.
These parasites feed once every two or three days. During the breeding season, the female can lay up to ten eggs daily. According to the height of laying eggs, it is possible to establish how long a person is suffering from pediculosis.
Pubic louses are much smaller in size, however, their limbs are much more powerful and massive, which strongly distinguishes these insects from other species.
Nits usually called lice larvae. They have a white color, and their sizes usually do not exceed 2 mm, so they can be easily seen in the hair.
In pubic lice, nits are much shorter compared to other varieties - their size does not exceed 0.4 mm. The form of nits always resembles a spindle, and they are attached to the hair with the help of a capsule that wraps the hair of a person as tightly as possible.
What if lice appear?
When lice have been detected, a pest control is first required, to which the following items must be subjected:
- Linens,
- Household items
- Clothing,
- Everything else that the sick person was in contact with.
Physical pest control implies washing at the highest possible temperature. The effectiveness of this method depends on how long the effect of a certain temperature will be.
The minimum figure should be 60 degrees - with her clothes should be stretched for at least half an hour. In the wet state, it will have to go with a hot iron.
If things are forbidden to be washed at such a high temperature, they should be frozen, however, this method is not very effective. It is used only if it is not possible to use other methods of exposure.
Lice usually calmly fall into low temperature, falling into anabiosis. At temperatures of -20 degrees, they are able to survive during the day.
What are dangerous lice and nits?
As mentioned earlier, lice feed on human blood, so they can carry all sorts of diseases, including quite dangerous - typhus, scabies and so on. This is the main danger posed by these parasites.
Another not too dangerous, but rather unpleasant effect that occurs in a person infected with lice is severe itching of the scalp or skin surface.
Ways of transmitting head lice
 Lice can easily pass from one person to another, especially in the following situations:
Lice can easily pass from one person to another, especially in the following situations:
- On long trips or business trips, when a person does not have the ability to follow basic rules of personal hygiene,
- When staying in seasonal jobs in the summer,
- In schools or in kindergartens, where children have been in close contact with each other for quite a long time,
- In crowded places, especially in such closed spaces as hospitals, clinics, trains, and so on.
Where to look for nits?
Usually, lice larvae are in the area of the hair roots - the female sticks an egg there, and usually does it at a distance of about 2-3 cm from the root. If the hair was already nit, then the female is unlikely to attach her egg there. Nits are usually whitish, so finding them in the hair is not too difficult.
To find them, you can find special combs that will peel the nits from the hair, shaking them off. In some cases, nits are found in the armpits, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard. A body louse usually sets aside nits in the seams of clothing. Pubic in terms of reproduction is not very different from the head.
Symptoms of Pediculosis
Usually, when this disease occurs, hair on the occipital and temporal part of the head is the most severely affected.
In principle, the symptoms of infection with lice of all varieties are approximately the same:
- A very severe itching, due to which a person can comb the skin literally to the blood,
- The skin areas infected with these parasites begin to rot, which causes boils and ulcers,
- If the disease is in the advanced stage, the skin becomes more dense, and periodically changes the pigmentation,
- With the naked eye, you can easily see the nits, fixed in the area of the hair roots.
Effective means of lice and nits
The best remedy for pediculosis today is the so-called repellentswhich not only drive out lice, but also scare them away.
These sprays contain only compounds that are safe not only for children but also for pregnant women. This tool can be applied to the skin surface, hair, things.
Causes of pediculosis
How to find out about infection with head lice? It has long been no secret that in places where there is a special "crowding" of people, it is likely that infection with various parasites, especially lice.
Contrary to popular belief, not only unscrupulous people are susceptible to infection with head lice, lice can get infected by prosperous citizens.

The main reason for the appearance of lice is the close communication of a healthy person with an infected person. Infected discovers this fact not immediately - after some time, when the parasites have multiplied.
Lice can hide for a long time from the eyes of a person, due to their small body size and ability to move quickly through the scalp.
To recognize the presence of lice, you need to know the features by which you can "calculate" the presence of this living creatures.
Lice species:
- Head
- Pubic (ploshchitsa).
- The dressing room.

Head lice live in the hair, easily moving through them. To do this, they are adapted processes on the legs in the form of claws. Externally, the louse is a very small insect, 2-4 mm in size. The color varies from light gray to light brown. After the louse is saturated with blood, its color changes to red. The insect has no wings. Feet short.
Pubic louse settles on the hairy areas of the genitals. Planters are never found in the head, they can live and move only along the vegetation of the body:
- scalp,
- pubic zone,
- armpit
- chest
The clothes louse lives in the folds of clothes:
Insects crawl on the skin of the human body in order to bite and suck the blood.
Distinguishing types of lice is necessary for their detection, since they live in different parts of the body.

Symptoms indicating infection with head lice
When a louse bites through the skin, its glands secrete a special enzyme that is irritating, causing itching. An unpleasant disease is complicated by the fact that lice multiply rather quickly, and then live in whole groups. Accordingly, the bites become a lot.
In places of louse bites remain papules - rashes, similar to mosquito bites, bedbugs.

People who are predisposed to allergic reactions, rash from bites grow, redden, increase. The wounds remaining after scratching become infected, inflamed, suppurate.
In people with low allergies, itching and rashes may be absent.
Pediculosis can be determined with the help of nits, these are lice eggs. Thanks to a special adhesive, nits are firmly attached to the hair.
On examination, it is immediately noticeable nits. Their shell has a whitish color, which indicates their presence in the hair, especially dark. Form nits egg-shaped, slightly elongated. If you squeeze the nits between the nails, its shell will burst, making a characteristic sound.
With a massive infection with lice, the hair will look like it is sprinkled with small grains.

Symptoms of lice on the head:
- Itching, worse in the evening and at night, mainly in the occipital region.
- Rash: papules, foci of inflammation, pustules, crusts.
- Feeling of insects crawling over the skin.
- Itching, observed even after washing.
- The appearance of nits is white.
- Waste lice: small black spots on the skin. Easily detected when falling on light clothes or bedding.
The presence of parasites is accompanied by more rapid pollution of the head.
It makes sense to look for parasites in the skin of the occipital and temporal areas of the head. It is here that the skin is the most delicate and thin. This is a favorite place lice, because here they are the easiest to bite through the skin.
Caution, pediculosis! How to get rid of the diseaseHow to determine the presence of lice
How to understand that you have lice, what to do when they are detected?
To determine the presence of parasites, a survey is carried out - you need to ask an assistant (family member) to examine the head. It is necessary to focus on those areas of the skin where there are traces of scratching, redness, small bleeding wounds, pustules. It is necessary to inspect carefully, scrupulously, especially paying attention to the examination of the skin of the occipital and temporal areas.
There is also a way for lice to self-detect:
- you will need a comb with frequent teeth and a light cloth (paper),
- you need to tilt your head in the direction of the spread fabric (paper) and carefully, slowly, comb your hair,
- you need to comb from the back of the head, gradually moving towards the forehead,
- comb teeth should be in contact with scalp.

It is possible that during this procedure, one of the insects will be able to be grabbed by the teeth of the comb, it will fall out and become noticeable on the light paper.
After combing, you should carefully consider the comb, between the teeth of which can be found stuck lice and nits. For people with poor eyesight, it makes sense to use a magnifying glass, due to the extremely small size of parasites that may go unnoticed.
Tip: Before you try to detect insects, you should wet your hair with water - lice can not move.
It is possible to understand whether there are lice on the head by the characteristic symptoms: itching, aggravated at night, not bringing relief, sores, pustules.
If you cannot detect lice yourself, you should consult a doctor: a dermatologist, a general practitioner.
Prevention
Infection with parasites occurs by the contact-household method.
- Pediculosis is easy to catch when using common hairbrushes, towels, hats. Everything must be individual.
- Remember that lice are transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person when they touch their heads.
- If there are cases of infection with lice in the kindergarten (school, kindergarten), it is better to temporarily limit its attendance.
- You can not swim in the same water with infected lice - in it lice remain viable for a long time.
- It is worth avoiding small populous reservoirs.
- Carry out preventive examinations in children.
- Be vigilant after a night's lodging in doubtful places (hostel, train).
Observing precautions will not have to get acquainted with pediculosis.
Short description
Lice (called in Latin Anoplura or Siphunculata) belong to the sub-order of ectoparasites, belong to the order of the eared parasites. The main source of food of these insects is the blood of the host (human or animal), which they suck after piercing the skin.

The disease caused by lice, doctors call "pediculosis." In general, on the body (head) of a person and near it, 3 types of these parasites live most often. These include: head, body and pubic lice, differing in location. We describe in more detail each of them.
Linen lice
The size of the linen lice is slightly larger than the head. The body can reach a length of 2-4 mm, is characterized by peculiar projections from the sides. No wings. The color of the chitinous layer is grayish, sometimes whitish. They can be found on the human body (affected area: back, limbs, sides), as well as in textile items (clothing, bedding, towels) and furniture (seams, pockets, decorative items).
There is a myth that lice are transmitted to humans from animals. In fact, this is not quite the right judgment. Animals can also parasitize lice, but they belong to another species. They will never eat human blood. So, there are deer, seals, camel, hare louse and others.
At what temperature lice and nits die, you will find on our website.

Features of the structure under the microscope
With the increase of individuals, you can see all the departments and their structure in detail. For example, what the piercing-sucking apparatus of this parasite looks like. It consists of 3 main organs:
- the mouth opening, where the chitin hooks are located, their function is to stick to the surface of human skin,
- stilettos - piercing needles (3 pieces) connected in a sting,
- pharyngeal tube - a kind of pump, transfers blood from the mouth to the intestine.
Also, when examining the lice under a microscope, one can clearly see the patterned contours of the body, the villi, segments of the antennae, hooks on the legs, segments and the design of the abdomen.
Subcutaneous lice
It has long been known that lice are external parasitic insects. Their body is not adapted to penetrate the skin of a person, but they can easily be held on to the hair, clinging to their strong legs. Even if the insect accidentally refuses to open the wound, then hurry out of there. It is noteworthy that the lice larvae cannot exist under the skin of their host. In this way, subcutaneous lice do not exist.
Where did the term "subcutaneous lice" then come from? Often scabies itchies (ticks) are taken for these insects, as they cause similar symptoms. So, a person notes an itch, the appearance of sores and blisters on the skin, but at the same time he cannot understand the reason for their occurrence.

How to search and how to remove from hair
If you suspect infection with lice in the first place you need to carefully examine the scalp. It is required to push the bunches of hair on the top and sides, carefully examining the skin and roots.
Another way is to use a comb with frequent teeth and try to comb out parasites. In any case, if you carefully examine the patient's skin, you can see a louse with the naked eye.
Note! When searching for parasites inspect a dry or wet head.
On wet hair
 Algorithm of action when detecting bloodsucking in this case, represented as:
Algorithm of action when detecting bloodsucking in this case, represented as:
- First you need to wash your hair with shampoo, and then apply a large amount of conditioner. Comb the hair with a comb with wide teeth
- replace the comb with a comb with frequent teeth. When combing, they should lightly touch the scalp and reach the hair roots,
- Slowly brush the hair from top to bottom. Insects should stay between the teeth,
- remove lice on time,
- wash your conditioner after brushing hair all over your head.
We recommend reading: technique and rules for combing lice from the head.
On dry hair
 When identifying insects on dry hair, do the following:
When identifying insects on dry hair, do the following:
- untangle the head of hair with an ordinary comb,
- comb with frequent teeth, brush your hair in small areas from the roots downwards (spend 3-4 times in one place)
- check if there are parasites left on the comb,
- comb all hair.
Finally. If you feel itching at different times of day, wounds began to appear on your head, then you should conduct a visual inspection of the hair roots, make a thorough combing.
If you suspect infection with lice, you need to go to the hospital to a dermatologist or pediatrician (for children) and start treatment immediately. The best way to get rid of lice - processing chemicals.
The following articles may be useful for effective control of head lice and nits:
- how to safely get rid of lice during pregnancy
- the danger of lice in humans, the effects of head lice,
- how to use the drug Full Marks (fullmarks), reviews,
- how effective is the Knicks shampoo for lice and nits,
- instructions for use of spray Pair Plus,
- The best remedies for lice and nits in children.
What kind of lice does a person have?
The human louse is an insect from the suborder of the eel of the order. There are 2 morphological types:
- head lice - live lice in their hair, voluntarily never leave their wearer,
- louses - live in the folds of clothes, use a person as a power source, they are not permanently on it, after saturation they take refuge in places of their settlement.
There is another subspecies of human parasites - the pubic louse (ploschitsa). Its name accurately reflects the localization. It is distinguished from its relatives by the special structure of the limbs. Depending on the type of insect, pediculosis, respectively, also happens to be clothes, pubic, head or mixed - with simultaneous infest of several types of parasites. Below are photos of human lice.

Appearance
Adult female sizes do not exceed 4mm. The males are slightly smaller - the maximum body length is 3 mm. In view of the tiny dimensions, the structure of the body can only be viewed enlarged under a microscope or with a magnifying glass.
Parasites have a transparent, flat, elongated body. Hungry individuals grayish-brown color. In the process of feeding, it becomes red, almost scarlet. If you watch the parasite at the time of absorption of food, you can see how the stomach is stretched and the body becomes more rounded.
Lice - very bloodthirsty individuals. They feed from 2 to 4 times a day, and the larvae up to 8 times per day. The female drinks 0.7 mg of blood.

3 pairs of legs with sharp claws are attached to the chest, thanks to which the blood-sucking insect moves freely in the hair. Spiracles are also located on this part of the body. On the head are simple eyes and antennae - organs of smell.
Mouth apparatus piercing-sucking type is represented by the following organs:
- a hole with chitinous hooks, through which the louse is attached and held on the skin,
- needles for piercing,
- the tube, which is like a pump, draws blood from the mouth into the intestinal tube.
Because of the short proboscis, the insect is forced to immerse its head in the wound, therefore, during the meal, it is in a perpendicular position in relation to the integument.
Nuances of parasitism
A detailed study of photos of lice in the hair can be seen that they are located mainly at the base of the hair follicles, that is, closer to the power source. These parasites are one of the few that remain loyal to their wearer. Only a cardinal decrease in temperature caused by the death of a person forces lice to leave their homes and go in search of a new food item.

The optimal temperature for lice is 27-28 ° C. With a decrease to 10 ° C, the vital processes slow down, reproduction stops. Subzero temperatures above 45 ° C are disastrous. Without food, head lice can live no more than 2 days. For the same amount of time, they preserve their vital activity when they are in the water.
There is a misconception that head lice appear only in people who rarely wash their hair. However, the appearance of bloodsuckers is not related to the frequency of hygienic procedures, since they do not feed on sebum or dead cells of the epidermis. Moreover, it is proved that lice move more comfortably in clean hair.
What the nits look like
The genitals are located on the abdomen. In the female, they are located in the ninth segment of the forked abdominal cavity and are called gonopods. In males, the sexual organ is represented by chitin stripes. After mating after 2-3 days, the female begins to lay eggs by 5-6 pieces per day. During her 35-45 day life, she manages to give life to 170-200 individuals.
Lice eggs are called nits. They are tiny size and do not exceed 1 mm. In the photo you can see that they are an oblong capsule with a lid. The female sticks nits to the hair with the help of a sticky substance that is released from the genopods. After 7-10 days under favorable conditions, the lice larvae leave the capsule, and the dry nits remain hanging on the hair. Externally hatched individuals do not differ about their parents, except for sizes.

Distinguishing nits from dandruff is easy enough. The eggs of the lice are visually the same size, when pressing on the nail plate, a characteristic creak appears. Dandruff is a dry dead cell, which can be of various sizes.
The youngsters begin to feed heavily, undergo 3 molts and in 6-10 days turn into mature individuals ready for breeding. Increase, decrease in temperature, dryness, insufficient moisture slow down the development of the larvae. Below are photos of nits on hair and dandruff.
Signs of head lice
During the meal, the parasite introduces an enzyme that prevents blood coagulation and an anesthetic substance, so that the louse bite is not accompanied by pain, and there is only a slight tingling sensation. Subsequently, the following symptoms of pediculosis appear:
- severe itching
- pustules, triggered by combing,
- insomnia,
- irritability,
- swelling of the lymph nodes
- in cases of long-term infection, the appearance of an unpleasant odor, purulent masses, sticking of hair, crusts, dry nits.
Detect irritant can be a visual inspection of the skin of the head. Without a magnifying glass, it seems that the hair is littered with dandruff. However, armed with a magnifying glass, you can see the nits along the entire length of the hair and crawling adults. In the photo of pediculosis, occipital, temporal, neck, behind the ears are most susceptible to bites.

Accumulation of more than 75,000 lice in the hair can be fatal. The psychological and neurological factor plays a significant role in this.
Pediculosis, like other diseases, needs treatment. To get rid of lice, carry out hygiene procedures with anti-pediculosis means and the subsequent combing of dead individuals and nits. Greatly simplifies the process of comb lice.
After her daughter returned from the summer camp, she noticed that she had dandruff. Sinned on a new shampoo, but after the change of detergent there were no changes. We went to see a dermatologist, and he determined that it was lice that had already managed to breed and lay eggs - nits, which we took for dandruff. For the treatment of pediculosis, they purchased the Nuda remedy and processed the head in accordance with the instructions. A week from the lice and nits, there was no trace.
Optimum breeding conditions
For laying eggs, the female should eat regularly and live in a comfortable environment for her + 30 ° С. Without food, an adult can live no more than a day. But being outside the human body, it is able to fall into anabiosis and stay in a “sleepy” state for several months.
Pubic louses retain vital activity in a 20-30 cm layer of sand up to 4 days, in water up to 2 days.
During her life, the female lays 50-60 eggs. Nits are attached to the base of the hair and as it grows they rise above the skin. The development of larvae occurs as in other species of this family. In the photo of lice and nits in the groin area, you can see in detail how pediculosis looks in the pubic area.

Symptoms of pubic lice
The incidence of pubic parasites is called pubic lice or phthyriasis. In most cases, the disease is sexually transmitted, therefore, recognized as venereal. If the infection has occurred through sexual contact, then pediculosis is often just one of the components of the venereal “bouquet”, so treatment should be carried out after consulting a specialist.
During a bite, a pubic louse injects an enzyme that prevents blood from clotting and dilutes it, thereby destroying hemoglobin and bluish spots up to 15 mm in size appear at the site of the bite. When pressed, they do not disappear. The following symptoms also appear:
- itching
- brown and black dots on underwear are traces of insects,
- with a strong scratching the occurrence of purulent wounds, blisters, peeling,
- development of dermatitis.
Sexual contact with a carrier of blood-sucking insects, which people call obscene words, is not the only way to infect head lice. Nits are well fixed on clothes, tissues, therefore women, men and even children are equally at risk of lice infestation. Contribute to this:
- joint sleep with an infected
- use of towels, clothes, bedding,
- visiting public places: beaches, baths, saunas, swimming pools.
In children, phthyriasis usually appears on the eyelashes or eyebrows.

It's a shame to talk about it, but I want to warn others to avoid my mistakes. I want to tell you how our joint holiday with my wife on the Black Sea coast almost ended in divorce. I have a habit of basking in the sun on the hot sand. I basically do not use litter, I want to be closer to nature, to feel its naturalness. A few days after the active sunbathing, began to feel itching in the intimate area. At first, he didn’t attach any importance to it, maybe this is my skin so sensitive to salt water. Then he began to notice that his wife, too, was scratching this notorious zone.
Upon returning home, her husband went to the gynecologist and returned, to say the least enraged. She started accusing me of infidelity and that I rewarded her with specific tricks. But I was 100% sure of myself, especially since adultery contradicts my life credo. We went together to the reception to the venereologist. He found pubic lice and me. The doctor asked in detail about the last places to visit and came to the conclusion that 99% of the infection was caused by me, but only indirectly. It is likely that I picked up the parasites, wallowing in the sand. So it is impossible to predict where lice come from.
Treatment of pediculosis is carried out under the supervision of a doctor or at home through a series of activities:
- shaving hairline greatly facilitates the process of getting rid of bloodsuckers, but is not a prerequisite
- Since the nits on the hair are attached with a sticky substance, a weak solution of vinegar is used to dissolve the adhesive component,
- affected areas are treated with appropriate sprays, shampoos, ointments, lotions: Nittifor, Medifox, Veda, Pedilin, Spey-Pax,
- disinfection of bedding, underwear.
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable, bloodsucking insects and nits can be eliminated in several procedures.
The best means of pediculosis for children
The most effective medicines for lice and nits today are the following:
- Pyrethrum - the special powder made from the Caucasian camomile. It is detrimental to lice and nits, but for a person it is absolutely harmless,
- Permethrin and its derivatives - inexpensive effective remedy for lice and nits. It can cause minor harm to health, but lice destroys much more effectively. May be used for children from the age of five,
- Methylacetophos for a person, it is rather toxic, with a louse ruthless, besides the effect of the drug lasts for several days, so relapse is excluded.
Regarding which remedy for lice and nits is better, there are many opinions, but it is better to follow the recommendations of the manufacturer.
Are nits passed from person to person?
The lice larvae themselves are immobile, therefore they cannot move, except with lost hair or on hairbrushes, hair elastics and so on.
Despite the fact that nits are noticeable relatively well on the hair, they will be practically invisible on the comb. In order to prevent such an infection, it is advisable to use only individual hair care products.
Testimonials for good pediculosis medications
 Reviews of drugs against pediculosis:
Reviews of drugs against pediculosis:
- Alena, 34 years old. Recently, a son brought head lice from a workout - well, that noticed on the same day. Thanks to the drug Nyuda managed to get rid of the disease almost immediately, only one day had to hold it locked up at home. All households also used this tool: the result was excellent, no other tool works so effectively.
- Vlada, 28 years old. As soon as the child was sent to kindergarten, an outbreak of pediculosis began, the caregivers even wanted to close for quarantine. We did not have a single louse, during the inspection did not find any nits - and all this thanks to the drug Paranite.
- Alexey, 40 years old. At work came from a hospital colleague. As it turned out, caught pediculosis. Immediately everyone was scared, someone advised a concentrated medifox. It is not too expensive, but thanks to him managed to prevent the spread of the disease.
Where lice come from
The main way of lice spreading is contact. Infection with head lice occurs when people are in close contact, which often happens in children's groups, in public transport, at public events, when using other people's hairbrushes, hats, clothes and linen.
Adverse sanitary and hygienic conditions are a major factor in the occurrence of lice. Clothes louse is often a companion of unsanitary conditions. However, the disease occurs in clean people. Lice outbreaks are recorded continuously. The peak of the disease is observed in the fall, when adults and children return from rest (pioneer camps, resorts).
Pediculosis in our country today is an acute problem. Up to 35% of all cases of the disease are common among persons 15 to 24 years old. 27% of cases are children under the age of 14 years. 16% of cases are adults 35 - 60 years. Often, pediculosis affects children from orphanages, boarding schools, and day-care centers.
In vagabonds, more often, pediculosis is registered, and pubic - among young people. Baby lice are transmitted from the mother.

Fig. 2. Lice infestation occurs when people and clothing come in close contact.

Fig. 3. The companion of unsanitary conditions is always pediculosis.
What the lice look like. Microbiology of parasites
In nature, there are about 200 species of lice. The insects that live on the human body belong to the Pediculid family (Pediculidae), the order Pseudorhynchota. Each species parasitizes only on a certain host and does not transfer to others. The head louse, pubic and clothes louse has epidemiological significance for a person.
Insects are carriers of some infectious diseases (typhus and relapsing fever, trench fever).
Lice feed on the blood of mammals that they inhabit. At one time, one individual is sucked up to 0.5 ml. blood. Fasting for 1 to 2 days causes insects to die.
When sucking blood, lice inject saliva into the skin. The saliva secreted by the parasitic bean glands irritates, resulting in inflammatory foci on the skin in the form of dense infiltrates, accompanied by itching, often very severe. Scratching sites are often infected with streptococci and staphylococci, which causes impetigo, folliculitis, and boils.

Fig. 4. At one time, lice suck up to 0.5 ml. blood. Males of parasites - 3 times less.
Lice die at temperatures above 45 ° C and below 0 ° C. If the ambient temperature decreases gradually and not much, the insects fall into a state of suspended animation, in which they can remain for several weeks without food.
In the folds of clothing and on the hair in places of greatest growth, lice lay eggs. The eggs in the cocoon are called nits.
Each species of parasite is characterized not only by a specific habitat, but also by the intensity of egg laying, feeding frequency, size and longevity.
Lice can be well examined under a microscope. In addition to the insects themselves, you can see 6 legs, cephalothorax, body segments, abdomen and antennae.

Fig. 5. In the photo insects under the microscope. Left - pubic, right - head lice.

Fig. 6. Head and body louses have an elongated shape (photo on the left). In pubic lice, the body is shortened, which is why they look like crabs (photo on the right).
The structure and nutrition of parasites
Oral organs of lice are able to pierce the skin and suck blood. The soft tube-trunk of the parasite is equipped with piercing needles, with the help of which the skin is punctured. The proboscis penetrates deep into the skin through rotational movements. The teeth of the end of the corolla cut through the stratum corneum of the epidermis. In the area of the dermal layer, flexible proboscis stilettos search for blood vessels. The wall of the detected vessel is cut by the stylet teeth and the proboscis is inserted into the vessel.
Next, the insect proceeds with bloodsucking, in which the pharyngeal pump contracts several times per second. Bloodsucking lasts a few seconds. During this time, about 1 mg of blood gets into the female's stomach. Due to the production of anticoagulant secretion, the blood does not clot. Nutrition lice occurs only in sedentary areas of the body.
Parasite eyes are often absent, or resemble two black dots. The oral organs lack the palpi. Antennas are short. The legs of the legs are short, the paws are single-segment, the front ends end with a sickle-shaped claw, thanks to which the louse is firmly held on the hair and body of the host.

Fig. 7. In the photo the head louse under the microscope (top view).

Fig. 8. In the photo lice under the microscope.

Fig. 9. The head of the parasite is separated from the chest. Taurus segments form a monolith.

Fig. 10. The body at the pubic louse is shortened (photo on the left), at the head and dress - elongated (photo on the right).

Fig. 11. The front pair of insect paws ends with sickle claws, due to which they are firmly held on the hair and body of the host.

Fig. 12. There are no palpi in the oral organs of the parasites. Antennas are short.

Fig. 13. In the photo to the left are louses during feeding. In the photo on the right, the parasite sucked blood, causing his stomach to swell.
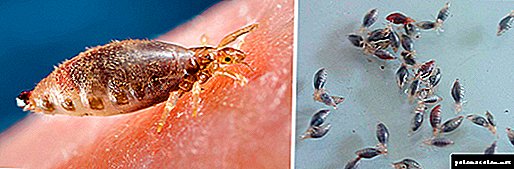
Fig. 14. In the photo are louses. After feeding, the insects become dark in color and become similar to bedbugs.
Breeding
Female individuals lay eggs 3 to 6 times per day. On average, an adult lives about 46 days. During this period, the female lays about 140 eggs. A cocoon is formed around the egg, which, due to the sticky secretion secreted by the lice, is attached and held for a long time on the hair. The egg and cocoon are called nits. The length of the nits is about 1 mm.
After 5 - 8 days the larva (nymph) leaves the nits. It looks like an adult parasite. The larva grows and develops 14 - 16 days. During this time, it molts 3 times. After the third molt, the nymph becomes an adult. Nymphs of the first period develop 5 days, the second - 8 days,
The cycle from egg laying to the first egg laying by the next generation ranges from 18 to 22 days. A temperature of 32-33 ° C is ideal for breeding. Under adverse environmental conditions, the reproduction of parasites slows down.

Fig. 15.In the photo the breeding cycle of lice from egg to egg, which lasts from 18 to 22 days.

Fig. 16. In the photo the transformation of a nymph into an adult.
Head louse
Head and body louses are very similar in appearance. They often interbreed with each other and produce offspring, change their “place of residence”. Both body and head lice are considered double species.
The head louse lives on the scalp, often in the back of the head, in the temple, on the beard and mustache in men. Due to the special structure of the legs, the insect is firmly attached to bunches of hair with a circular cross-section.
The insect has an elongated shape; its length is 2–3 mm, the length of the female’s body is 4 mm. The body of the parasite is transparent or has a grayish-yellow color. On the sides there is a sharp pigmentation.
Lice only crawl. From person to person, they crawl through towels, bed linen, combs, etc. They can be picked up in the train carriage, on the beach, in the store and in the pool.
Louse lays eggs 4 - 5 times a day. Over the course of a lifetime, the number of eggs laid reaches 120 - 140. The maturation of eggs lasts 7 to 10 days. Most often, eggs are laid in the ear region and the lower part of the occiput.
Head lice feed 1-2 times a day. After absorption of blood, the belly of the insect becomes purple. The volume of blood sucked by the female at a time is about 0.7 ml. Males suck blood three times less. Without food, the head louse dies after two days.
The life expectancy of insects is from 28 to 38 days.

Fig. 17. In the photo, a head louse (adult) and a nit.

Fig. 18. After absorbing blood, the belly of the insect becomes purple.
Pubic lice
Due to the special structure of the paws, pubic lice are firmly attached to tufts of hair with a triangular cross-section. Insects live in the area of the pubis, perineum, scrotum, perianal fold, rarely - on the edge of hair growth on the head, in the armpit, eyelashes and eyebrows. Transmission of lice from person to person is carried out by sexual and contact routes.
Pubic louse has a length of 1 - 2 mm. Female insects are larger than males by one and a half times. The parasite has a wide short belly, with the result that its appearance resembles a crab. The color of the pubic lice is dark in color. Parasites move slowly. Females lay up to 3 eggs per day. In all her life, one female lays about 30 eggs.
Attached by the mouths of the follicles to human skin, pubic lice feed almost continuously, with the result that the patient is constantly worried about itching. The life expectancy of insects is from 21 to 28 days.

Fig. 19. In the photo louse pubic and nit.

Fig. 20. In the photo of the habitat of the pubic lice - the pubic region (left) and eyelashes (right).

Fig. 21. In the photo pubic lice in the armpit.
Linen lice
Body lice or laundry lice, despite their inactivity, spread quickly to people on contact. Particularly often infected with parasites in places where homeless people live, refugee camps and various types of shelters (tents, tents), children’s long-term stay in kindergartens and schools, public transport, public baths and saunas, hiking trips, cheap hotels and children's camps .
Parasites live and lay eggs in the folds and the area of the seams on clothes and underwear, on clothes - most often in the area of the belt, collar sleeves and cuffs.
The body louse is larger than the head one, has an elongated abdomen and a uniform gray color. In length adult individuals make 3 - 5 mm.
Linen lice eat 2 - 3 times a day. For food insects crawl on the skin, most often the lumbar region and neck. Egg laying occurs 6 to 14 times a day. In all her life, one female lays 180 to 200 eggs.
The lifespan of body lice is 4 weeks in males and 1.5 - 2 months in females.
The clothes louse dies at a temperature below 13 ° C and above 60 ° C. This allows you to get rid of parasites by non-chemical methods (washing clothes and freezing).

Fig. 22. On a photo a linen (wardrobe) louse and its nits.

Fig. 23. Nymphs and adult bed lice (lingerie) seem transparent (photo left). Adults of the pubic and head parasites darken slightly (in the photo on the right).

Fig. 24. The photo shows a cluster of lice on clothes (photo left) and synthetic insulation (photo right).
What is nits
Female lice lay eggs on average 3 - 6 times a day. On average, an adult lives about 46 days. During this period, the female has time to lay about 140 eggs.
Head lice live from 28 to 38 days. Females lay eggs 4 - 5 times a day. Over the course of a lifetime, the number of eggs laid reaches 120 - 140. The maturation of eggs lasts 7 to 10 days.
Pubic lice live from 21 to 28 days. Females lay up to 3 nits per day. In all her life, the female lays up to 30 eggs.
Body lice live from 1.5 to 2 months. Females lay eggs 6 - 14 times a day. In all her life, one female lays 180 to 200 eggs.
How do lice eggs ripen
Female lice and pubic lice lay eggs on different hairs. When running pediculosis, laying eggs can occur on the same hair.
It takes 5 - 8 days from egg to larvae. This process is influenced by ambient temperature. The optimum temperature for incubation is 33 ° C.
Larvae and lice die at temperatures above 45 ° C and below 0 ° C. If the ambient temperature decreases gradually and not strongly, insects fall into anabiosis, and the development of eggs slows down. At low temperatures, egg development may stop for several months.
Due to the frequent cooling of clothing, louse eggs can develop much longer than head and pubic lice eggs. The hatched larva is able to crawl.

Fig. 26. In the photo to the left the moment of opening nits. First, the cap is separated from the nits. Air enters its cavity, which accumulates at the base and gradually squeezes out the larva. In the photo on the right is the time of release of the larva.

Fig. 27. In the photo on the left there is a nit in which the larva matures. In the photo on the right view of the nits after the release of the larva.

Fig. 28. In the photo nits on the hair.

Fig. 32. In the photo are pubic louses and nits.

Fig. 34. In the photo pubic louses and nits on the hair of the pubic zone and eyelashes.

Fig. 35. In the photo linen louses and nits.



